Text to RL: Extracting High-Quality RL Questions from text
The Data Challenge in Modern RL
Reinforcement learning has demonstrated exceptional potential in solving complex problems, but a critical challenge looms as we scale these systems: we’re facing a severe shortage of high-quality RL questions. Current public datasets max out at just at around a million questions—below what’s needed to push next-generation RL systems to their full capabilities. This scarcity becomes even more pronounced outside the mathematics domain, where well-structured RL questions are particularly rare in domains like biology and physics. To achieve the full potential of RL, we need to expand our training data by orders of magnitude across diverse knowledge domains.
Our Approach: Synthetic Question Generation from Textbooks
We propose a straightforward yet powerful method for generating vast quantities of high-quality RL questions by leveraging existing textbook content. Here’s how it works:
- Extraction: We feed textbooks page by page into an LLM that extracts potential questions and solutions naturally embedded in the educational content.
- Verification: Each extracted question passes through a verification LLM that confirms solvability using only the provided textbook content.
- Filtering: We remove questions that depend on visual elements like tables, figures, or diagrams, ensuring our dataset consists of purely text-based, self-contained problems.
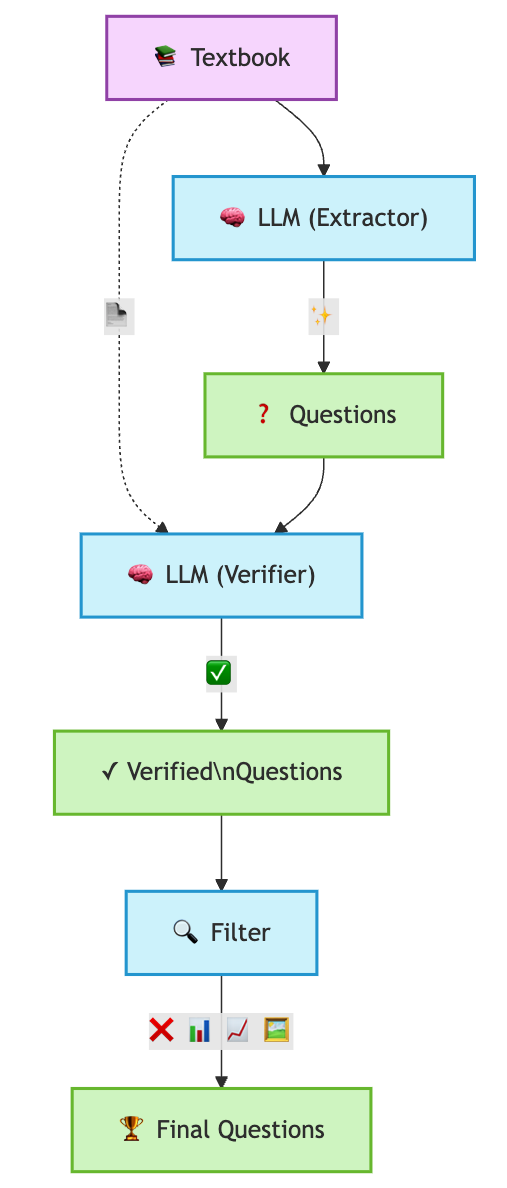
This pipeline allows us to generate around ~3000 valid questions per textbook, creating a scalable approach to building massive RL datasets.
Experimental Validation
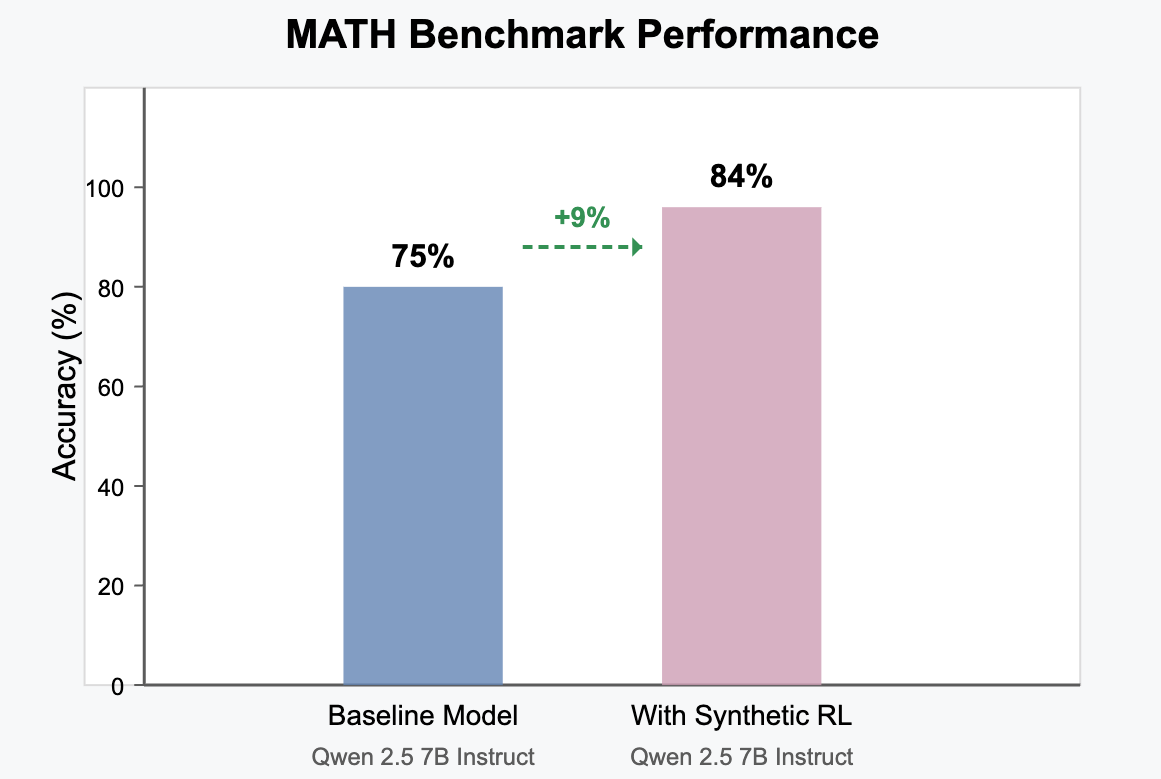
To validate our approach, we trained Qwen 2.5 7B Instruct on these synthetic questions and measured performance improvements on the MATH benchmark.
- Models trained on our synthetic dataset showed a 9% absolute improvement on MATH, increasing performance from 75% to 84%. Performance was still improving run simply ran as proof of concept of effectiveness of synthetic RL questions
- This significant jump demonstrates that these synthetic RL questions provide a strong reinforcement learning signal
- The results suggest we can effectively bootstrap model performance using generated content
Opensource Dataset
As part of our commitment to advancing the field, we’re open-sourcing a sample dataset of 100K problems. This dataset provides researchers and developers with immediate access to high-quality synthetic questions for RL training and experimentation.
Discussion
As RL training becomes central to advancing model capabilities, the demand for high-quality training questions will continue to grow exponentially. Our textbook extraction approach offers several critical advantages that address current limitations:
- Token Efficiency: Perhaps the most profound implication of our work is the inherent efficiency of RL training with targeted questions compared to traditional next-token prediction. As models advance, structured questions may provide more learning signal per token than standard predictive training. While promising, rigorous ablation studies are needed to quantify this efficiency and determine optimal training approaches.
- Domain Expansion: While mathematics has benefited from existing question datasets like MATH, fields such as biology, physics, chemistry, and medicine lack comparable resources for RL training. Our extraction pipeline works equally well across disciplines, generating high-quality questions from biology textbooks about protein folding, physics textbooks on quantum mechanics, or medical texts on diagnostic reasoning.
- Adjustable Difficulty: The pipeline naturally extracts a range of question difficulties, but we can also engineer specific difficulty curves by generating hints alongside questions or by tuning extraction parameters. This enables curriculum learning approaches where models progressively tackle harder problems.
- Customizable Content: Beyond difficulty tuning, we can target specific subdomains or reasoning types by selecting appropriate textbook sources or by fine-tuning our extraction criteria.
Conclusion
Our synthetic question generation approach offers a viable path to scaling RL training data by orders of magnitude. The initial results demonstrate that these synthetic questions drive meaningful performance improvements in trained models.
As we continue to refine this approach, we believe it will become an essential tool for advancing the frontier of reinforcement learning capabilities. The virtually unlimited supply of textbook content gives us confidence that we can generate the billions of diverse, high-quality questions needed for the next generation of RL systems.
Resources
-
Code Repository: BeyondNextTokenPrediction on GitHub
